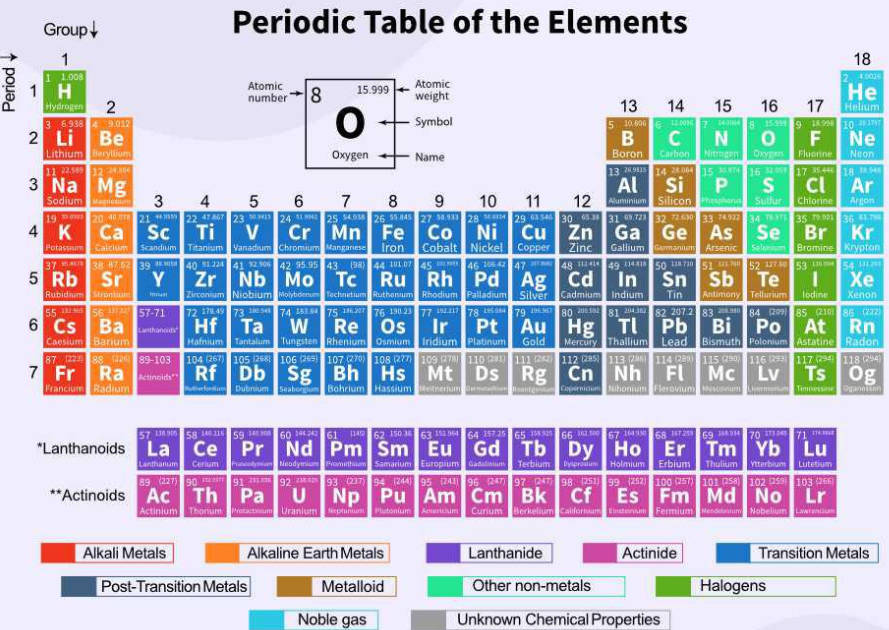
Chemical elements are systematically arranged in the Periodic Table according to their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurrent chemical characteristics. It is one of the most crucial instruments in chemistry and acts as a guide for comprehending how various elements are related to one another.
Elements:

Key Features of the Periodic Table:
Atomic Number: Denoting the quantity of protons in an atom’s nucleus, the elements are grouped in ascending order by atomic number.
Periods: In the periodic table, the horizontal rows are referred to as periods. The contemporary periodic table is divided into seven periods, each of which denotes the number of electron shells present in the atoms of the elements in that row.
Families or Groups: These terms refer to the vertical columns. Because they share the same number of electrons in their outermost shell, elements of the same group exhibit similar chemical characteristics.
Element Symbols: A distinct one- or two-letter symbol, such as H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, or Au for gold, designates each element.
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids:The elements in the periodic table can be classified as follows: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Nonmetals are normally located on the right, metalloids in a zigzag line between the nonmetals and metals, and metals on the left and center.
Elements in Groups:
(Group 1)Metals classified as alkali : very reactive.
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals: Less reactive than alkali metals.
(Groups 3–12):metals that are usually hard and have high melting points are classified as transition metals .
Group 17: Halogens: Nonmetals that are reactive.
Group 18: Noble Gases: Very low reactivity inert gases.
Electron Configuration: The Periodic Table presents the elements’ electron configuration as well. The elements are arranged according to their valence electrons, or the electrons in the outer shell, which play a major role in determining their chemical behavior.
History and Development:
Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, created the periodic table for the first time in 1869. Mendeleev put the 63 known elements in a table according to their atomic masses, allowing space for elements he thought might yet be discovered. Later, his table was improved and rearranged according to atomic number, creating the current periodic table that is in use today.
Significance:
Predictive Power: Scientists can forecast the characteristics of elements, even those that were unknown when Mendeleev conducted his research, thanks to the Periodic Table.
Chemical Reactions: Because elements in the same group frequently behave similarly, it aids chemists in understanding how elements interact in chemical reactions.
Education: Periodic Table is a vital resource for teaching chemistry since it enables pupils to comprehend the connections between different elements.
READ MORE: Why Gold Is Expensive?
Conclusion:
In summary, the Periodic Table is a useful tool that summarizes the essential ideas of chemistry and is much more than just a list of elements. Its systematic grouping of atoms according to electron configuration and atomic number reveals the underlying patterns in their properties, making it a vital tool for understanding atomic structure, forecasting chemical behavior, and finding new elements. Periodic Table, which connects the macroscopic features of matter with the microscopic world of atoms, is a monument to the elegance of scientific research. Its status as one of the most significant scientific discoveries in history is further evidenced by its ongoing relevance in research, education, and business.










