Introduction
Top 10 Highest Populated Animal In the World Ever wondered which creatures dominate our planet in terms of numbers? From microscopic organisms to visible wildlife, Earth’s biodiversity is immense. Understanding the most populated species is crucial for appreciating nature’s balance and the ecosystems’ dynamics. This article dives into the top 10 highest populated animals, revealing fascinating insights into their world.
Factors Influencing Animal Populations
Animal populations are shaped by several factors, including:
- Natural Habitat: The availability of resources like food, water, and shelter.
- Reproductive Strategies: Animals that reproduce quickly and in large numbers tend to dominate.
- Human Impact: Activities like urbanization, agriculture, and climate change significantly affect population sizes.
Top 10 Highest Populated Animals
1. Ants
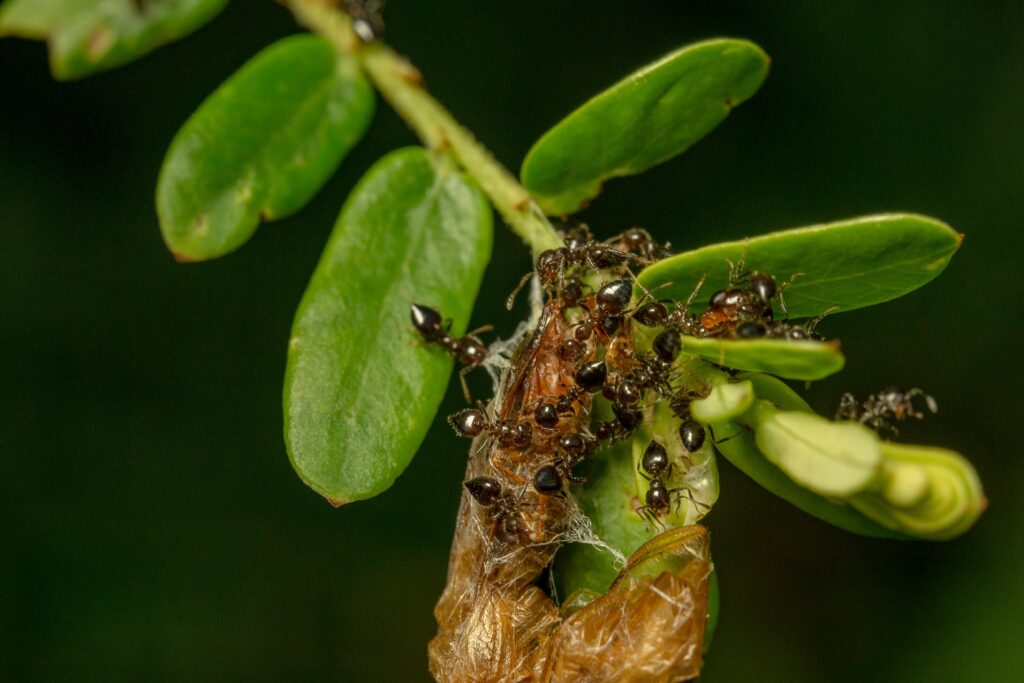

Ants are everywhere—literally! With over 10 quadrillion individuals worldwide, ants are arguably the most numerous animals on Earth. They thrive in diverse ecosystems, from rainforests to deserts. Known for their teamwork, ants aerate soil, decompose organic material, and support food chains. Their small size and social structure make them resilient and prolific.
2. Krill
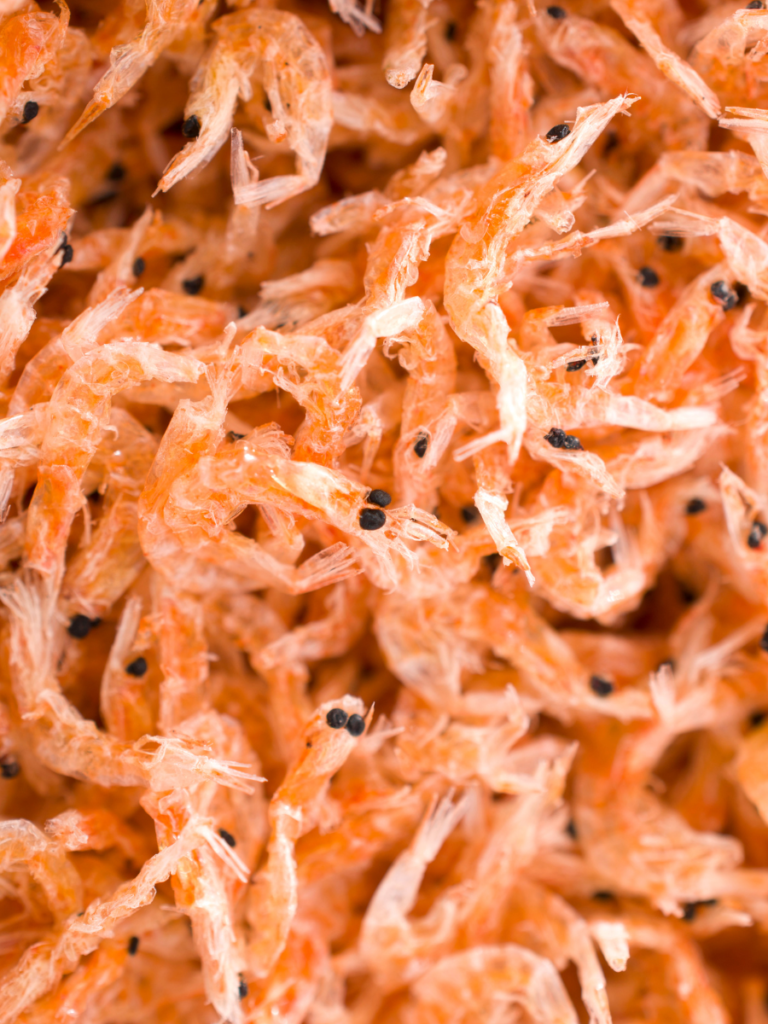

Krill, the tiny crustaceans found in oceans, boast an estimated population of 300-400 trillion. They form the foundation of marine ecosystems, serving as a primary food source for whales, seals, and seabirds. These small but mighty creatures are vital for maintaining the health of the oceans.
3. Termites
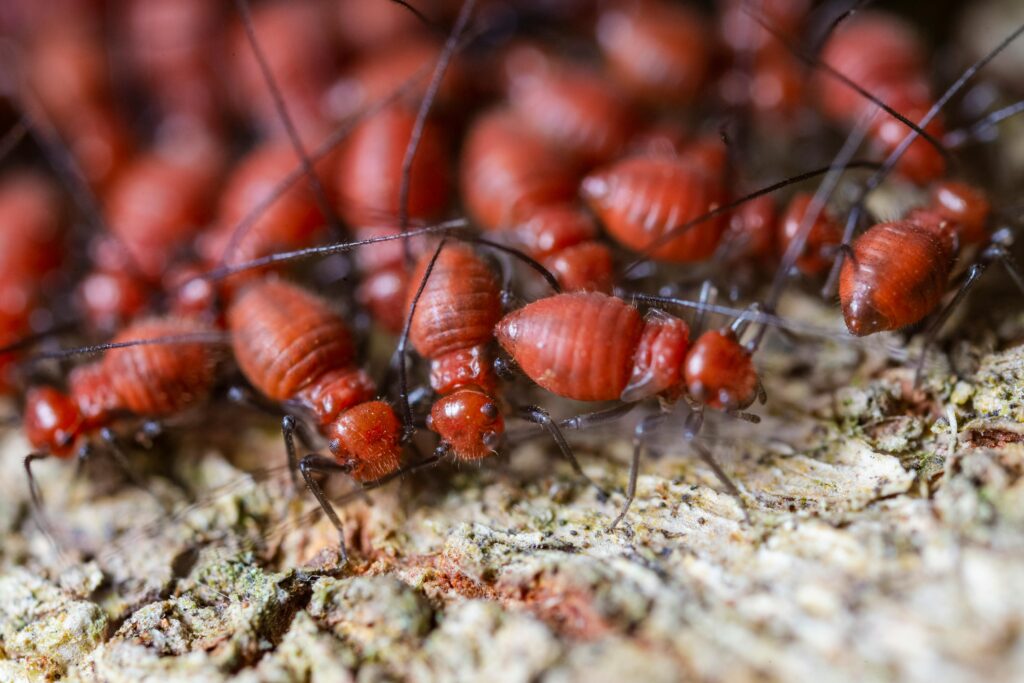

Termites may be pests to humans, but they’re ecological powerhouses. Found primarily in tropical and subtropical regions, their population is estimated in the trillions. These insects play a key role in breaking down dead plant matter and recycling nutrients, ensuring soil fertility.
4. Bacteria (E. coli)
Though not an animal in the traditional sense, bacteria like E. coli are among the most populous living organisms. Found in the intestines of humans and animals, as well as in soil and water, E. coli populations are uncountable. These microorganisms are vital for digestion and the planet’s nitrogen cycle.
5. Mosquitoes
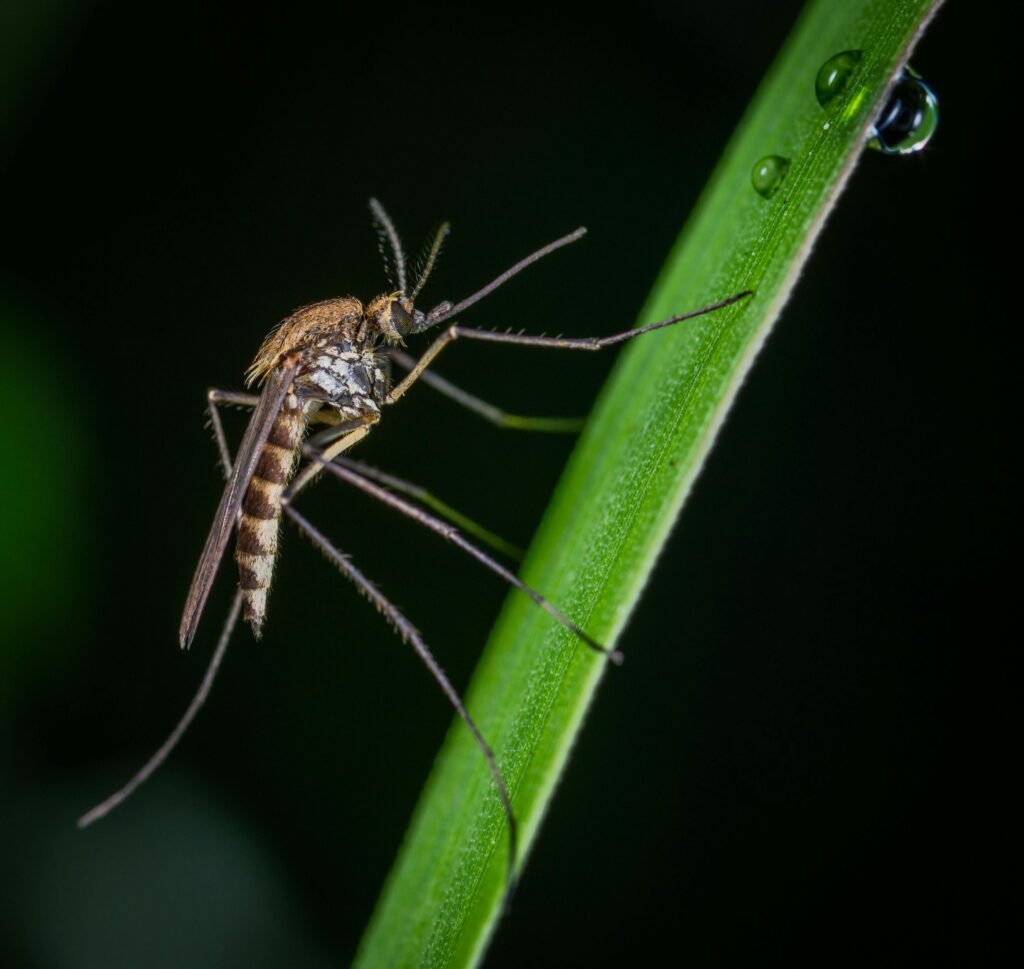

Mosquitoes, often unwelcome guests, number in the trillions. These insects thrive in warm climates and are known for their role in spreading diseases like malaria and dengue. Despite their reputation, they are a key food source for many birds, bats, and amphibians.
READ MORE:10 Endangered Species
6. Fish (Bristlemouth)

Bristlemouth fish, primarily found in the deep ocean, are the most abundant vertebrates on Earth. Their population is estimated in the hundreds of trillions, making them vital to marine ecosystems. These small, bioluminescent fish play a critical role in the ocean’s food web.
7. Chickens
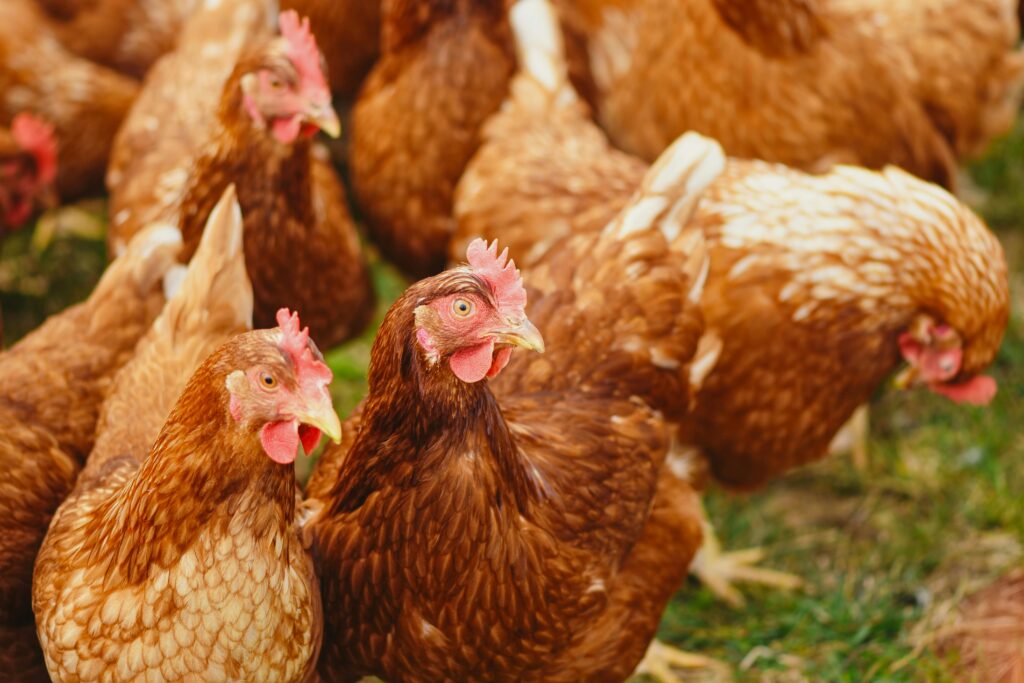

Chickens are the most populous domesticated birds, with over 25 billion individuals worldwide. Their population explosion is directly linked to human consumption of eggs and meat. Chickens are an integral part of global agriculture and food systems.
8. Humans
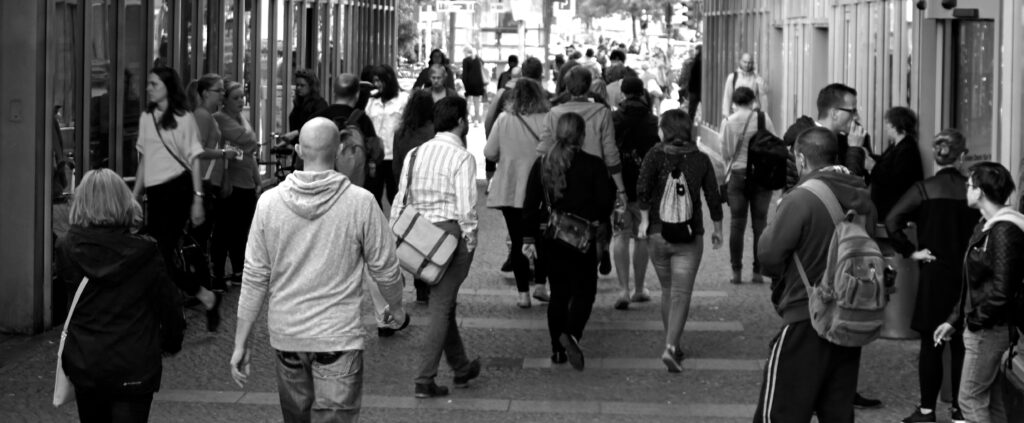

Humans, currently numbering over 8 billion, have become a dominant force on Earth. Our adaptability and intelligence have allowed us to inhabit nearly every corner of the planet. However, our activities have significantly impacted other species and ecosystems.
9. Rats
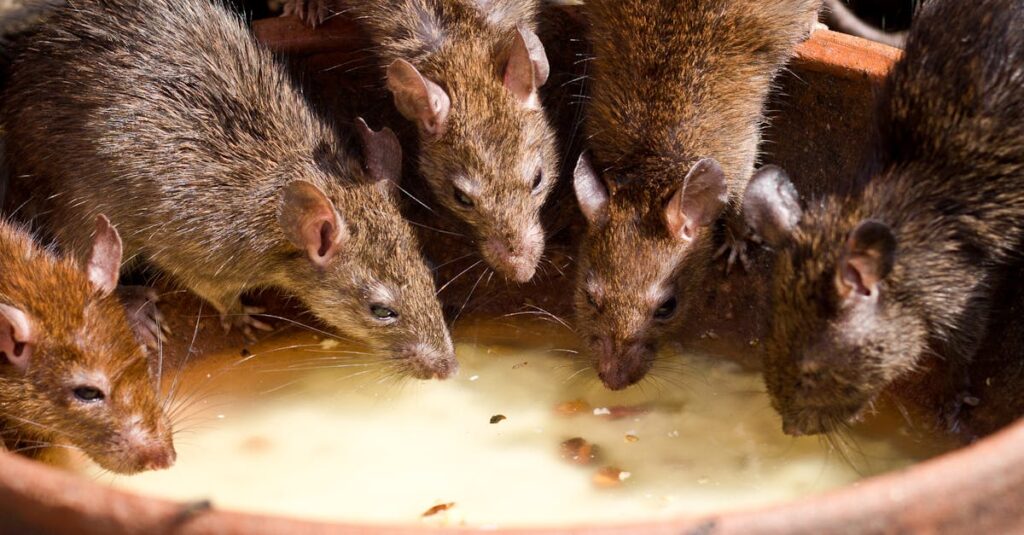

Rats are incredibly adaptable and thrive wherever humans are. With billions of individuals worldwide, they’re often considered pests. However, they also play an important role in scientific research and urban ecosystems.
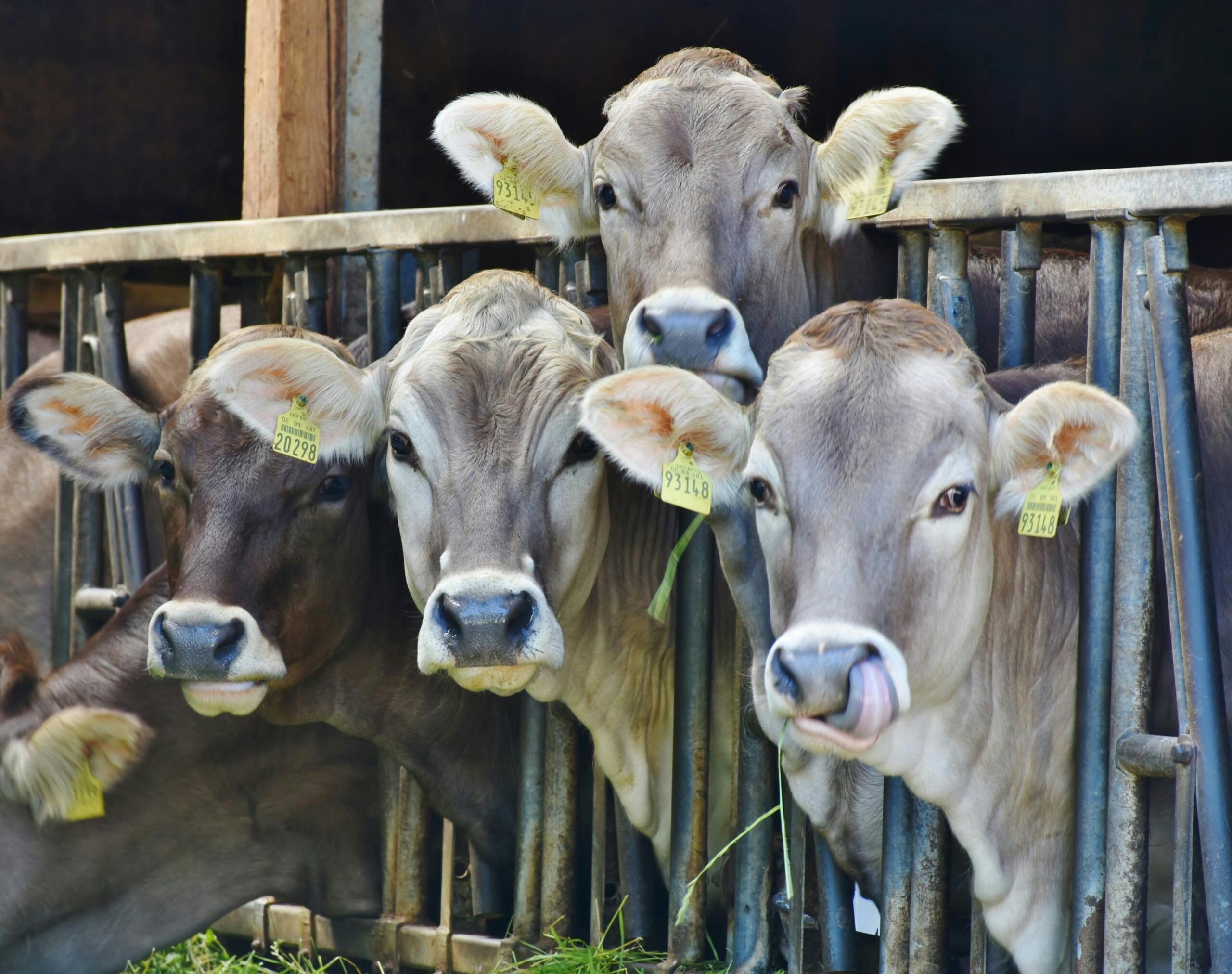
10. Cows
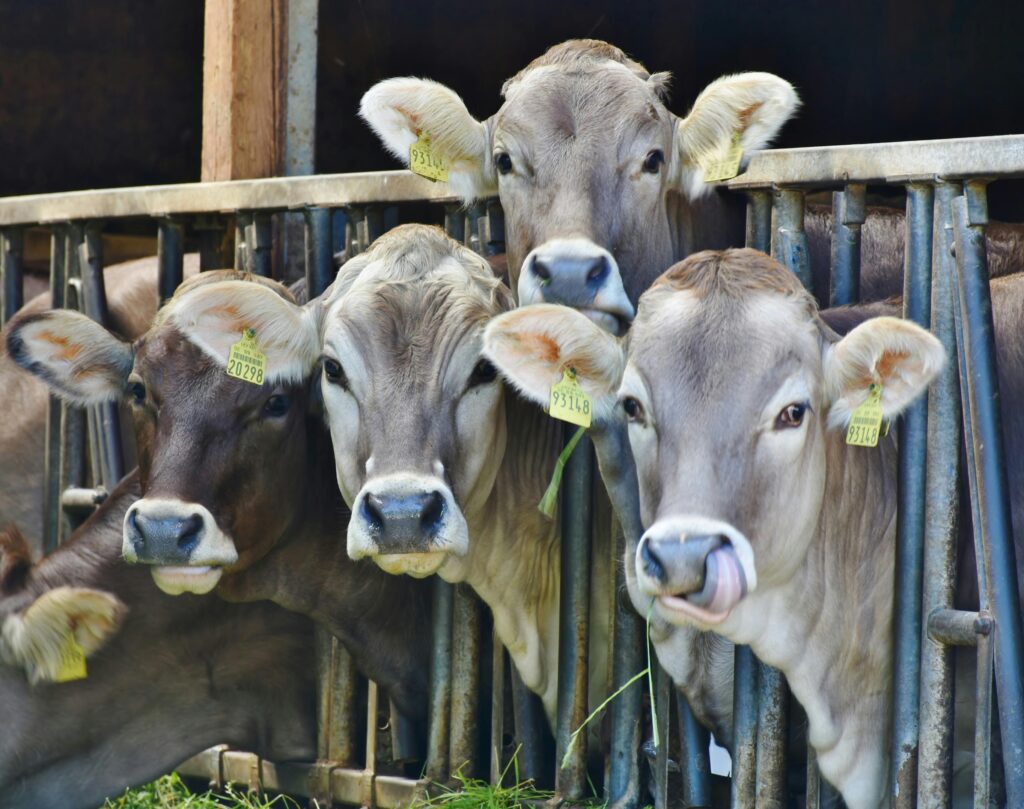

With a global population of over 1.5 billion, cows are among the most populous domesticated animals. They provide milk, meat, and labor, making them indispensable to human societies. However, their large numbers contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
Why Understanding Animal Populations Matters
Tracking animal populations isn’t just a numbers game—it’s a necessity for:
- Ecosystem Health: Large populations indicate stable ecosystems, while declines signal potential ecological issues.
- Conservation Efforts: Knowing which species are thriving helps prioritize resources for endangered species.
- Biodiversity: Understanding population dynamics highlights the interdependence of life forms.
Challenges in Estimating Animal Populations
Despite advancements in science, estimating animal populations is far from easy:
- Remote Habitats: Animals in oceans, dense forests, or underground are hard to count.
- Elusive Species: Some animals are naturally secretive, making them difficult to study.
- Technological Limitations: While drones and satellites help, they have their limits in accuracy.
Steps Toward Sustainable Coexistence
Humans play a crucial role in maintaining animal populations. Here’s how we can contribute:
- Conservation Policies: Protecting natural habitats and endangered species.
- Reducing Pollution: Lowering our environmental footprint to protect ecosystems.
- Educating Communities: Spreading awareness about the importance of biodiversity.
Conclusion
The world is teeming with life, from the tiniest krill to the ever-adaptable rats. Each species, regardless of its population size, plays a unique role in Earth’s ecosystems. By understanding these dynamics, we can work toward a future where humans and wildlife coexist harmoniously.
FAQs
1. What is the most populated animal in the world?
Ants, with an estimated population of over 10 quadrillion, are the most populous animals globally.
2. Why is studying animal populations important?
It helps us understand ecosystem health, conserve biodiversity, and predict environmental changes.
3. How do human activities impact animal populations?
Activities like deforestation, pollution, and climate change can either increase pest populations or drive species to extinction.
4. Which animal is the most adaptable in urban areas?
Rats are incredibly adaptable, thriving in urban environments and often coexisting with humans.
5. How can we help maintain biodiversity?
Conservation efforts, reducing pollution, and raising awareness are key steps toward preserving biodiversity.











